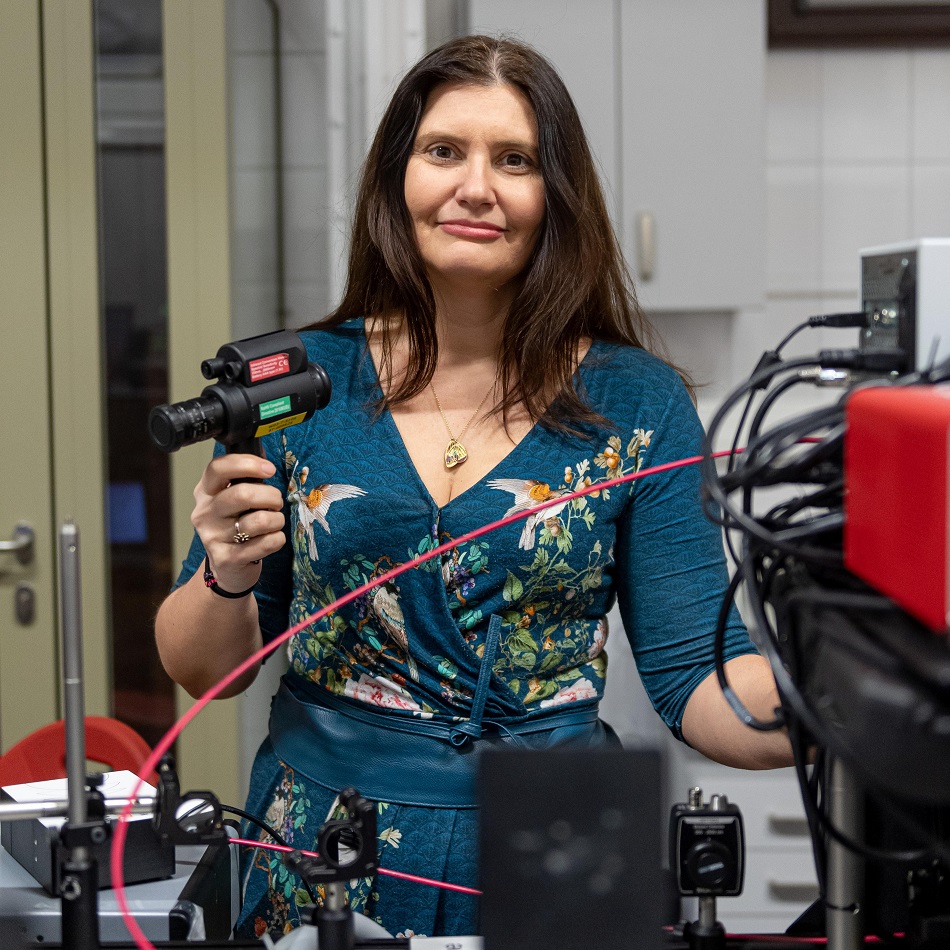
A paper on the role of a light source in antibacterial photodynamic therapy has been published in the prestigious journal Chemical Society Reviews. Its co-author is Professor Katarzyna Matczyszyn from the Faculty of Chemistry at Wrocław University of science and Technology.
Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (APDT) is a new and promising approach to combating the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance. It is based on the action of a photosensitiser, light and oxygen.
“In our publication, we compare different light sources, which are crucial in the process of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy”, says Prof Matczyszyn.
Many studies on APDT confirm its efficacy in vitro and in vivo against bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites. However, the development of the field is focused on exploring potential targets and developing new photosensitisers. The role of the light source, a key element for ROS production, has so far been overlooked.